IoT SIM Cards
Datablaze offers complete IoT scalability by providing the best IoT SIM card and data plan for each device in your IoT deployment – plus manage all your devices in one data management platform.
Connect your IoT devices in 220+ countries with over 675+ carriers.
Datablaze allows you to choose the best IoT SIM card with a data plan and carrier network for each IoT device required for your deployment. Whether you have ten SIMs or thousands, single-carrier or multi-carrier, you will also have exclusive access to Voyager, Datablaze’s IoT management platform.
Robust SIM Management Platform
4G/LTE, 5G
LTE-M (Cat M1)
NB-IoT
Detailed Data Usage Reporting
Secure Environment
IoT SIM cards allow wireless IoT devices equipped with cellular modules to connect just about anywhere around the world where cellular service is available. Given the diverse nature of IoT applications, each requiring distinct data plans and network connections, the ability to select tailored IoT data plans and carriers ensures seamless connectivity across various locations while optimizing costs.
Here are just a few of our operators.
We've partnered with the best wireless carriers.
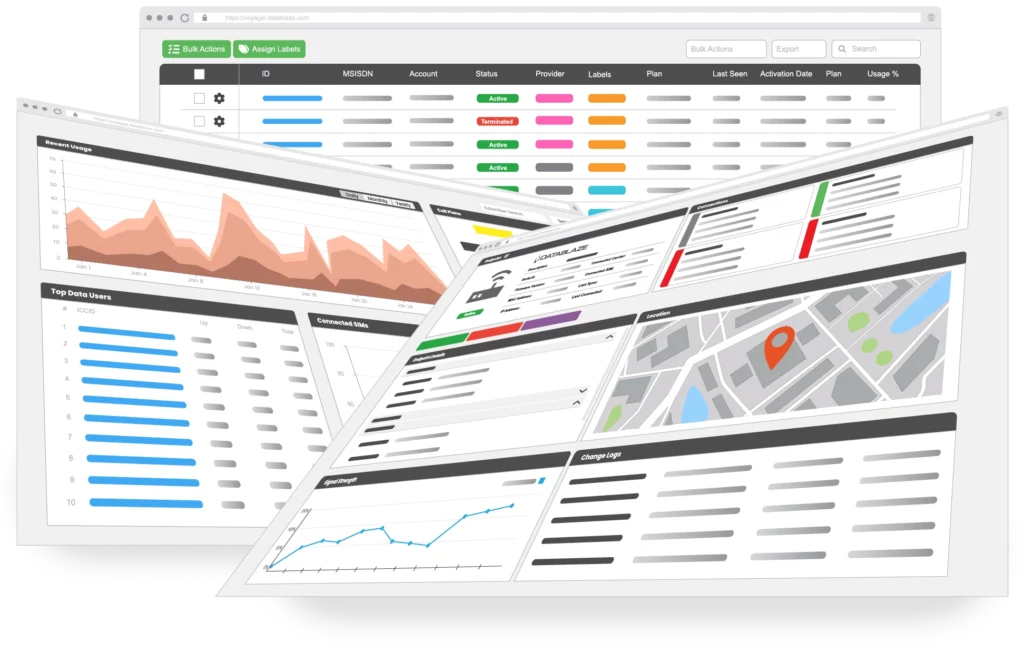
Scalable All-in-One SIM Management Platform
Effortlessly oversee your Datablaze ONE multi-carrier SIMs alongside single-carrier SIMs and existing subscriber agreements, all within a unified platform. VOYAGER seamlessly integrates all cellular connectivity subscriptions, streamlining the management of data plans, usage, and billing.
- Activate, suspend, or terminate IoT SIM cards
- Send alerts to users before exceeding limits
- Visualize historical and real-time data usage
- Comprehensive API suite
What is an IoT SIM Card?
A SIM card, or Subscriber Identity Module card, is a small electronic chip that is inserted into mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices, to authenticate and identify the device on a cellular network. SIM cards store information such as the device’s unique identification number, mobile network credentials, and subscriber data.
In the context of IoT, there are specific SIM cards known as IoT SIM cards or M2M SIM cards (Machine-to-Machine SIM cards). These SIM cards are specifically designed for IoT devices that require cellular connectivity to send and receive data to and from other devices or device management platforms.
Unlike traditional SIM cards used in consumer mobile devices, IoT SIM cards primarily focus on providing reliable and cost-effective data connectivity rather than voice and text services. IoT devices typically rely on cellular data plans to transmit and receive data, which can include sensor data, telemetry, monitoring information, and other machine-generated data.
In IoT deployments, multiple devices are often connected, each equipped with an individual SIM card. This enables each device to have its own cellular connection and data plan. Managing and controlling these SIM cards and associated data plans in a centralized manner is made possible through a SIM management platform like VOYAGER. Such a platform allows administrators to activate, monitor, and manage the SIM cards, provision data plans, track data usage, and perform other necessary tasks to ensure efficient and secure connectivity for IoT devices.
M2M SIM Security
An IoT SIM data plan from Datablaze will have the option to use dynamic or static IP addresses. Static IP addresses provide a secure way of connecting to wireless devices that my need maintenance, pushed updates or need hardware configuration.
To connect wireless IoT devices securely a VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is often used. This will ensure more sensitive data being transmitted to and from the device is encrypted. This blocks users outside the network from intercepting or interpreting the data. With IoT SIMs you can connect to your devices through a VPN for a more secure connection.
SIM Card Form Factors
Wireless devices are designed to accept a specific size SIM card. In most cases our IoT SIM cards are shipped as a 3-in-1 card with the ability to work with any of these 3 sizes.
- 2FF (Mini) – 25mm x 15mm – The original industry standard of all SIM form factors, used in larger wireless devices.
- 3FF (Micro) – 15mm x 12mm – About half the size of the mini-SIM, typically this size is used in mobile devices.
- 4FF (Nano) – 12.3mm x 8.8mm – A newer, smaller form factor designed to reduce space in small wireless devices.
eSIM – Also known as an embedded SIM card, are built into the IoT device. The SIM is embedded within the device by the OEM therefore, the card is not removable or interchangeable.

IoT SIM Card FAQs
Traditional SIMs are usually for consumer products such as smart phones and tablets. M2M SIMs will typically be subscribed to NB-IoT, CAT-M1, LTE and 5G business data accounts in bulk. Since the uses usually require data transmission only, voice is not often a feature used with these type of SIM cards. In some cases, M2M SIM cards are offered as industrial SIM cards. These cards are designed to withstand wear, higher vibrations, and more extreme temperatures.
SIM cards are provided in 3 standard sizes: 2FF, 3FF and 4FF. Some SIM cards are provided with all 3 sizes in one card, known as triple cut, but other cards may only be one specific size. The acceptable size is determined by the manufacturer of the device or wireless modem it will be installed in. If you are not sure what size is needed, check with your device manufacturer or SIM provider.
2FF (Mini) – 25mm x 15mm – The original industry standard of all SIM form factors, used in larger wireless devices.
3FF (Micro) – 15mm x 12mm – About half the size of the mini-SIM, typically this size is used in mobile devices.
4FF (Nano) – 12.3mm x 8.8mm – A newer, smaller form factor designed to reduce space in small wireless devices.
Carriers will often allow their SIM cards to roam across other networks when signal is poor or nonexistent. A steered SIM card will always connect to the main providers network even if signal is weak. If no coverage is available, then the SIM will be steered to the least expensive network that is available. A non-steered SIM will allow the device to determine which network to connect to, often based on the best signal strength detected.
An APN (Access Point Name) increases security by handling the authentication and security protocols on the IoT SIM card. An APN can be considered the entry point for cellular IoT devices because it serves as a gateway between the cellular network and the internet. It also can manage the type of traffic from other networks whether it is a private network or the internet.
A public APN is often provided by many mobile network operators (MNOs) which comes with basic configurations. Public APNs can also come with static public IP addresses, which is when the APN will assign an IP address and be unique to that device each time it connects to the network.
Private APNs let you customize your configurations and network settings. A private APN is simple if you are on an APN backed by a software-defined network (SDN).
Just about any device connected to a local or wide area network is distinguished by an IP (Internet Protocol) address. Most of these devices use dynamic IP addresses appointed by a DHCP server, where the network provider assigns the IP address for each device connected to it. This means it could change each time the device connects to the internet.
In case of static (fixed) public IP addresses, the device is assigned one IP address that will not change over multiple sessions. Static IP addresses are commonly used when the device will need to be securely accessed for monitoring and maintenance, regardless of location. Use cases such as security monitoring needs access to CCTV solutions to make it easier to monitor remote cameras.
Datablaze provides various options for IoT SIM cards. You can choose from multiple carriers and data plans to find the most cost-effective and best service for your application. Data plans purchased through Datablaze also gets access to its SIM management platform. The platform provides complete visibility of active SIMs, appointed data plans and their data usage.
These terms are used interchangeably. IoT standing for internet of things, is a term used for devices that typically do not require much human interaction. They include sensors, smart devices, wireless routers, and IO switches. An M2M SIM or machine-to-machine is often used when referring to SIM cards used for machines. The SIM cards typically are not different in any way.